News
Underwater Volcano is the Largest in the World – Comparable in Size to Olympus Mons on Mars
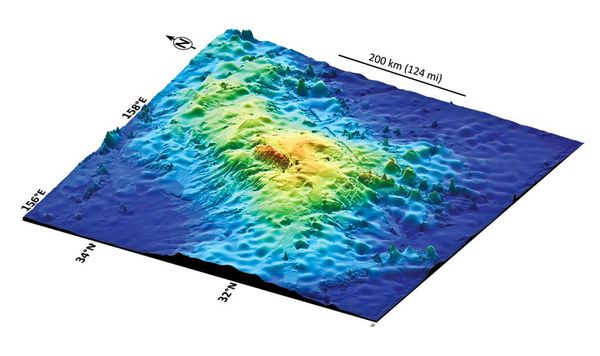
A giant volcano the size of New Mexico or the British Isles has been found under the Pacific Ocean, about 1,000 miles (1,600 kilometers) east of Japan, making it the biggest volcano on Earth and one of the biggest in the solar system.
Called Tamu Massif, the giant shield volcano had been thought to be a composite of smaller structures, but now scientists say they must rethink long-held beliefs about marine geology.
“This finding goes against what we thought, because we found that it’s one huge volcano,” said William Sager, a geology professor at the University of Houston in Texas. Sager is lead author in a study about the find that was published this week in the peer-reviewed journal Nature Geoscience.
“It is in the same league as Olympus Mons on Mars, which had been considered to be the largest volcano in the solar system,” Sager told National Geographic.
Tamu Massif is a rounded dome that measures about 280 by 400 miles (450 by 650 kilometers), or more than 100,000 square miles. Its top lies about 6,500 feet (about 2,000 meters) below the ocean surface, while the base extends down to about 4 miles (6.4 kilometers) deep. Tamu Massif dwarfs the largest active volcano on Earth, Mauna Loa in Hawaii, which measures about 2,000 square miles (5,200 square kilometers).
Made of basalt, Tamu Massif is the oldest and largest feature of an oceanic plateau called the Shatsky Rise in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. The total area of the rise is similar to Japan or California.
Sager started studying Tamu Massif about 20 years ago. He named it Tamu Massif because Tamu is short for Texas A&M University, where the scientist worked at the time; massif is French for “massive” and is a scientific term for a large mountain.
Scientists had known about the Shatsky Rise since the early 20th century, when it was first mapped, he explained. “We knew it was a big mountain range, but we didn’t know what the structure was like or how it formed,” said Sager.
He added that Tamu Massif is different from classic seamounts, the volcanoes that protrude off the ocean floor around the world by the tens of thousands. Tamu Massif is much larger, with a much more gentle slope than classic seamounts, Sager said.
Near the summit of Tamu Massif, the slope is only around one degree, he said. Down the flank the slope is half a degree, and it’s even less than that near the base. (The average slope of a staircase is 40 degrees, and an easy ski slope is about 10 degrees.) ”If you were standing on the massif, you would have a hard time knowing which way is down,” said Sager.
Finding an Unusual Structure
Scientists had thought the giant Shatsky Rise formed over time as a composite of several volcanoes that grew together, in a process similar to the way the big island of Hawaii was made by the outpourings of five separate volcanoes that were in close proximity.
But when Sager and colleagues looked at seismic data of Tamu Massif, they were surprised at what they found.
“We saw what appear to be lava flows going out from the center of the volcano in all directions, with no obvious large secondary source of volcanism, so that was a surprise,” Sager said.
The team also performed geochemical analysis on core samples taken from the massif. They found that the huge structure appeared to be made out of the same rock, of the same age.
So the scientists concluded that Tamu Massif was created by a single volcano, and probably over a relatively short period of time of a few million years. The volcano went “extinct,” meaning inactive, shortly after it formed, Saged added. That was probably in the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous period, about 145 million years ago.
“If what they are saying is correct, that is truly a massive volcano,” said Brian Jicha, a geologist at the University of Wisconsin who has received funding from National Geographic to study the formation of the Aleutian Islands.
“There are a lot of these oceanic plateaus, so if some of them really are just volcanoes, this paper might begin to change the way we think oceanic plateaus are built, and maybe even some of the continental basalt plateaus,” said Jicha, who was not involved in the study.
Sager agrees that more work is needed on other oceanic plateaus. “There could be around a dozen of these things out there,” he said about the possibility of more large shield volcanoes under the sea.
Sager noted that although Tamu Massif currently appears to be the largest single volcano on Earth, there are still larger volcanic complexes, such as theSiberian Traps, which may hold other mysteries. Those features were likely made up of molten rock from different sources, he said, unlike Tamu Massif’s formation according to the new theory.
How Did the Volcano Form?
Sager said scientists are still trying to work out the details of how Tamu Massif formed.
He said it seems likely that the spot on the seafloor had the right mix of elements, including a boundary of three tectonic plates, thin crust, and a source of hot magma below that was able to bubble up to the surface. The molten rock poured out, and then built up a wide, gradual rise as it cooled.
Precisely how the magma made it to the surface is an open question. Perhaps a blob of the rock got superheated, and then rose to the surface due to buoyancy. Or, cracks in the overlying crust could have opened, allowing molten rock to spill out.
The next step will be more work to figure out what the source of the magma was, said Sager. He would like to go back and measure the magnetic properties of the rock, using a ship that is equipped with GPS. The data will give him a better idea how the lava spread out, he said.
Jicha added that “if it is indeed really one volcano, and the case is fairly compelling, the amount of magma that had to go through the lithosphere [crust] is off the charts.”
“Not only does [Tamu Massif] give us a new wow in the form of a giant new volcano, but it gives us new insight into a building block of an oceanic plateau,” said Sager.
He’s not sure if the new volcano will help scientists better understand Olympus Mons on Mars, but noted that “we can see the surface of Mars better than we can see the bottom of the ocean.”
Tamu Massif, he said, “has been hiding out for 145 million years because it found a good place to hide.”
Source: National Geographic
Gear News
Introducing the TR-80, IR-50 and CS-30 Regulators from DYNAMICNORD

Whether you are a beginner or a professional diver – with the three new main regulators from DYNAMICNORD, everyone will find their favourite regulator. They all look super stylish.
Excellent performance with the TR-80
Quality and performance are the be-all and end-all for regulators. It is not for nothing that the TR stands for Tec Reg. The innovative design of the TR-80 guarantees absolute reliability – even in ice-cold waters.

Perfect breathing effort at 0.8 J/l / certified for diving in waters below 10 degrees / structural design made of solid brass for best cold protection / membrane-compensated design with dry seal of the first stage / reduced exhalation effort thanks to optimized exhalation membrane and bubble deflector / adjustable Venturi (dive/predive) and adjustment knob for individual inhalation comfort / innovative design of the front cover prevents free-flow in strong currents or when diving with scooters / design made of sandblasted brass, matt chrome finish / 2 HP and 4 LP outlets / mouthpiece made of high-quality, anti-allergic silicone for maximum comfort.


Amazing underwater adventures with the IR-50
The IR-50 is the top regulator for advanced and experienced divers. Natural breathing is the essence of this regulator.

Ideal breathing effort at 0.8 J/l /certified for diving in waters below 10 degrees / compensated membrane / adjustable venturi (dive/predive) and adjustment knob for individual inhalation comfort/ outlet valve and deflector for minimum exhalation effort and reduction of bubbles on the face / design made of sandblasted brass, matt chrome finish / 2 HP and 4 NP outlets / mouthpiece made of high-quality, anti-allergic silicone for maximum comfort.


The Workhorse – our CS-30
For diving centres and diving beginners – the workhorse stands for strong construction, reliability and robustness. Perfect for your training.

Optimal breathing effort at 0.8 J/l /recommended for diving in waters above 10 degrees / non-compensated piston / adjustable venturi (dive/predive) / outlet valve and deflector for minimum exhalation effort and reduction of bubbles on the face / design made of sandblasted brass, matt chrome finish / 1 HP and 3 NP outlets / mouthpiece made of high-quality, anti-allergic silicone for maximum comfort.


Octopus OP-30
The OP-30 is the ideal addition to all DYNAMICNORD regulators. It is identical in construction to the CS-30.

The TR-80, IR-50, CS-30 (DIN & INT) regulators and the Octopus OP-30 are available from DYNAMICNORD dealers and in the online store.
DYNAMICNORD – Your Outdoor Companion.
Marine Life & Conservation
Paul Watson Released as Denmark Blocks Japan’s Extradition Bid

Renowned anti-whaling activist Paul Watson has been released from custody in Greenland after spending five months in detention. Denmark’s Justice Ministry rejected Japan’s request for his extradition, citing insufficient guarantees that his time already served in custody would be credited against any potential sentence.
The 74-year-old Canadian-American was arrested on July 21 in Nuuk, Greenland’s capital, when his ship docked to refuel. His arrest was based on a 2012 Japanese warrant related to a 2010 encounter in Antarctic waters. Japan alleged Watson obstructed operations and caused damage to a whaling research ship during efforts to disrupt illegal whaling. Watson has consistently denied these claims, maintaining his commitment to marine conservation.
Denmark, which oversees extradition matters for Greenland, concluded that while the legal conditions for extradition were met, the lack of assurances from Japan regarding time-served credit made extradition untenable.
In a video shared by his foundation, Watson expressed gratitude and relief, saying, “After five months, it’s good to be out… and good to know they’re not sending me to Japan.” He added that the most difficult part of his time in custody was being separated from his two young sons.
Watson is a pioneering figure in marine conservation, known for founding the Captain Paul Watson Foundation in 2022 after decades of activism with the Sea Shepherd Conservation Society. His bold efforts to defend marine life have earned him widespread support, including from celebrities and conservationists. His work has also been featured in the acclaimed reality TV series Whale Wars.
Watson’s lawyer, Jonas Christoffersen, praised the decision, stating, “We are happy and relieved that Paul Watson is now free.” He added that Watson is eager to reunite with his family and continue his vital work.
The arrest occurred while Watson’s vessel, the M/Y John Paul DeJoria, was en route to the North Pacific with a team of 26 volunteers to intercept a Japanese whaling ship. His foundation described the arrest as politically motivated and emphasized that Watson’s actions were focused on ending illegal whaling practices.
Japan resumed commercial whaling in 2019 after leaving the International Whaling Commission, asserting that whale meat is a cultural tradition. Conservationists, however, continue to challenge these practices, highlighting their impact on marine ecosystems.
Despite the challenges, Watson remains steadfast in his mission to protect marine life and bring attention to whaling practices. His dedication to ocean conservation has made him a globally respected advocate for the environment.
-

 News2 months ago
News2 months agoIconic SS United States to become the World’s Largest Artificial Reef
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoBook Review – 52 Assignments: Underwater Photography
-

 Gear News3 months ago
Gear News3 months agoDYNAMICNORD – New German diving brand enters the British market
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoExploring Cenote El Pit: A Diver’s Dream
-

 Gear News3 months ago
Gear News3 months agoTry BARE drysuits (and maybe even win one!) this Friday with Sea & Sea at North West Dive Fest
-

 Marine Life & Conservation3 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation3 months agoBook Review: Coral Triangle Cameos
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoDive the Egyptian Red Sea this Autumn with Regaldive
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months ago2024 Ocean Art Underwater Photo Competition Announced















