Marine Life & Conservation
The Children’s Clean Ocean Summit

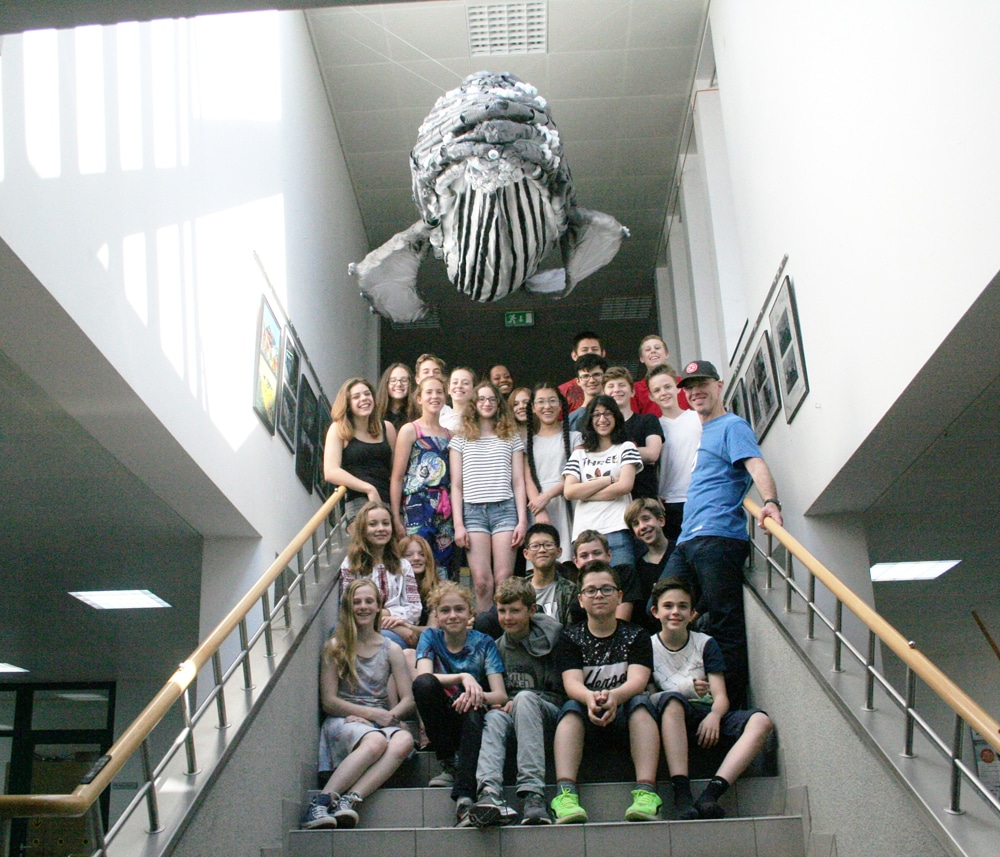
 This past June, nearly 300 kids from six Austrian schools gathered for the world’s first Children’s Clean Ocean Summit, titled “The Last Whale” and held at the United Nations in Vienna. The summit was run entirely by kids and involved them exploring the complex issue of plastic ocean pollution, teaching each other about solutions, then each voting for the three they found most critical. The summit culminated in the signing of their Children’s Clean Ocean Declaration, which shares their feelings and priorities and will be delivered to all world governments.
This past June, nearly 300 kids from six Austrian schools gathered for the world’s first Children’s Clean Ocean Summit, titled “The Last Whale” and held at the United Nations in Vienna. The summit was run entirely by kids and involved them exploring the complex issue of plastic ocean pollution, teaching each other about solutions, then each voting for the three they found most critical. The summit culminated in the signing of their Children’s Clean Ocean Declaration, which shares their feelings and priorities and will be delivered to all world governments.
The echoes of that event continue to resonate, finding their way so far into articles in six languages across the globe, and now to the world of scuba. It was an unprecedented event and may hopefully mark the beginning of new possibilities for children to powerfully participate in our world’s environmental narrative.
Here, Founder of the Kids Save Ocean Project, Peder Hill, shares their story:
How the Project Started – The Last Whale Sculpture
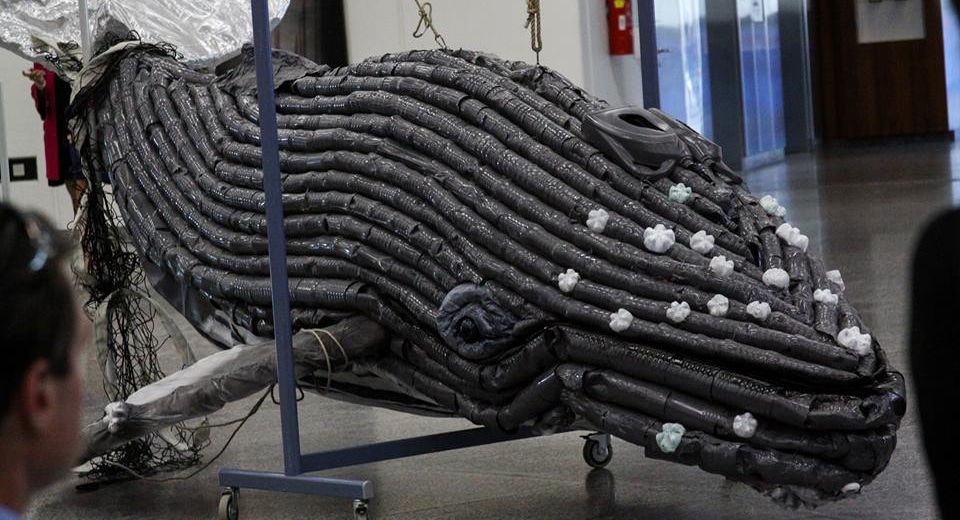
Children are deeply horrified by the growing tragedy of ocean plastic pollution. And two years ago the 12-year olds at my school and I (Peder (Mr. Hill), their art and biology teacher), decided to bring attention to the issue by building a 15-foot long humpback whale sculpture made from the same rubbish that desecrates our ocean’s beauty. We titled it “The Last Whale” in recognition of what will happen if we don’t change. After building it, however, we felt it wouldn’t change anything hanging in our school, as beautiful as it was. If it would have any impact, that whale, in spirit and in reality, would have to swim far beyond.
So we approached the United Nations with the concept of the summit, which they embraced, beginning a collaboration that would also include installation of the whale sculpture at the UN for the week that included World Environment Day and World Oceans Day, fulfilling its purpose. The whale is also scheduled for exhibition at Austria’s biggest aquarium, the Haus des Meeres, in 2020, after a new wind is finished. We’re seeking additional placements if you happen to know anybody.
The Project’s Massive Growth
I deeply believe that giving children a voice is vital to humanity’s future. And it turns out I definitely wasn’t the only one. To run a massive summit with just a teacher and a handful of scrappy passionate kids wouldn’t have been possible, so I turned to the global platform VolunteerMatch, and very quickly wonderful people from around the world joined me with the goal of empowering kids to not just learn about plastic ocean pollution, but DO something.
Hundreds of volunteers have come forward, including six app developers who are coding my Fatechanger app, an education and lobbying app designed to give kids a voice. Though unfinished, the app has already been taken up by the German Federal Ministry in its Ocean Plastics Lab international traveling exhibition, which showcases the contribution of science to understand and tackle the problem of plastics in the ocean. I’m currently in the process of forming the Kids Save Ocean non-profit to bring the project to scale.
20 Years Before in Cali
Long before fate swept me to Vienna, Austria, where I’d form the Kids Save Ocean project, and before the 200-plus volunteers flooded in to help me give kids a voice about the ocean and before the whale and the Summit at the UN and before being contacted by CNN about our efforts. Before all that, 20 years back, I remember a bolt blue sky above a clear Santa Cruz morning as my sister and I explored the hills of kelp heaped along the beach, washed up by the monster waves of a huge storm the night before. In amongst it were packages and containers from Japan, fishing gear, tourist beach trash, cigarette buts, even an ocean-cold Budweiser, which we promptly cracked and downed on the spot. Among piles of kelp, the global scatterlings of plastic junk.
In the two decades since that sunny harbinger of a morning, additional billions of pounds have accumulated in our seas, each piece of which will break down into tinier and tinier pieces, releasing toxins and being mistaken for food for hundreds of years. In another 20 years, what will our oceans look like? A frightening question.
Why form the Kids Save Ocean non-profit? Children deserve a voice in this world for one. And maybe, maybe, empowering them with a voice may be the help we so desperately need.
A Future: the Kids Save Ocean Mission Statement
Our core mission is to give children everywhere a voice about our planet’s environment, a mission we currently approach through our mobile app development, our work with the United Nations, and our exhibitions. Integral to that mission is providing teachers with a platform to deeply engage their students about plastic ocean pollution and the critically related issue of sustainability. We’re currently moving toward becoming a dynamic youth-centered non-profit to give children a powerful voice both now and forever.
For more information please visit the Kids Save Ocean website by clicking here.
Blogs
Evolution of Manatees in Florida
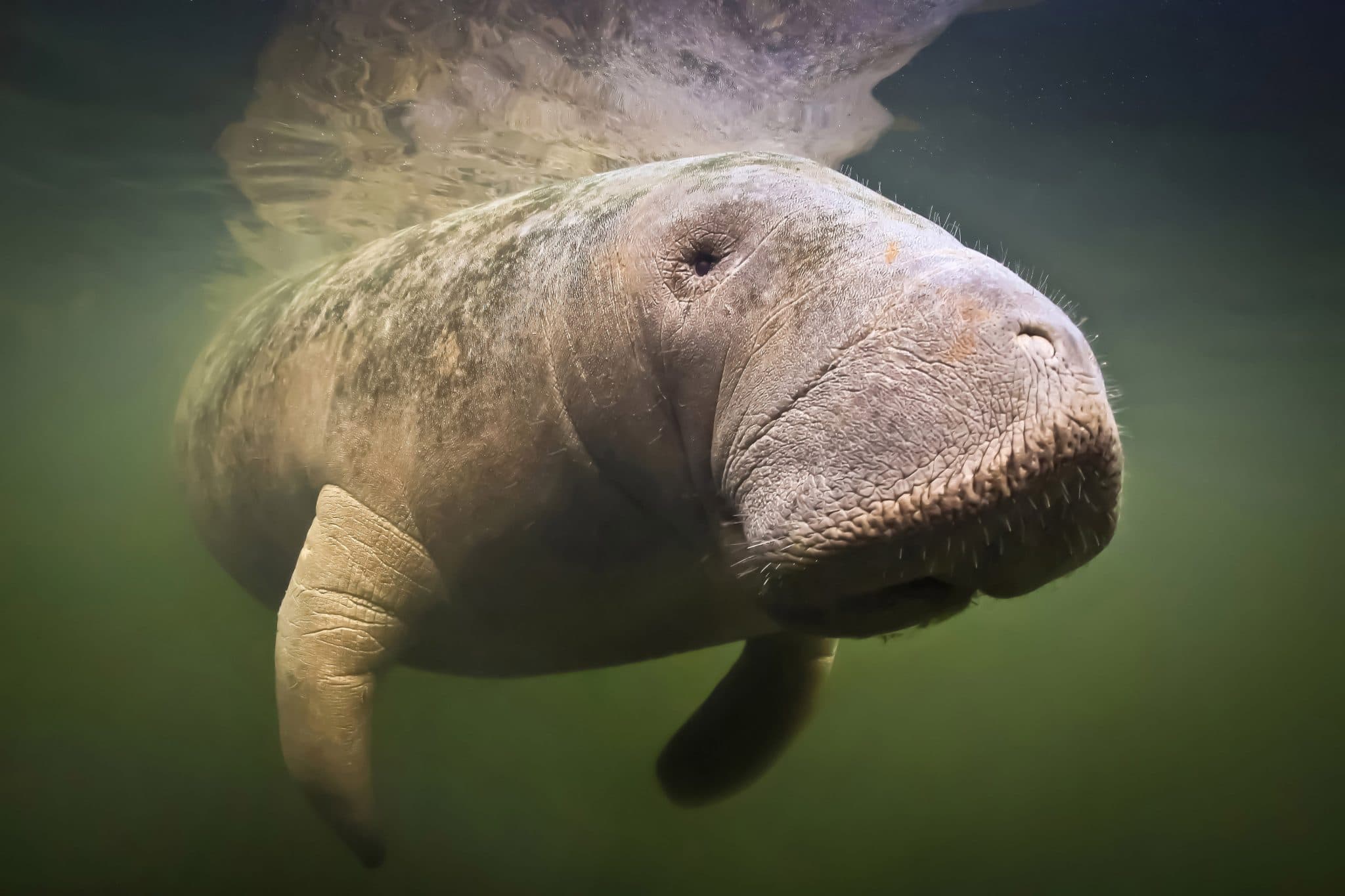

Op-ed by Beth Brady, PhD, Senior Science and Conservation Associate, Save the Manatee® Club
Recent news articles and broadcasts have claimed that manatees are not native to Florida or only arrived on Florida’s west coast in the 1950s. These claims, based on limited anthropological records, point to where manatees were historically exploited by humans and assume that a lack of evidence means manatees were absent from certain areas. However, absence of evidence is not evidence of absence—it’s like looking for stars in the daytime; just because you can’t see them doesn’t mean they’re not there. Moreover, genetic and fossil evidence indicate manatees have been present in Florida for the last 12,000 years.
The Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC), which manages Florida manatee populations, has created a manatee timeline highlighting key dates and notable information about manatee presence in Florida (https://myfwc.com/education/wildlife/manatee/timeline/). Historical records suggest that manatees have been observed in Florida as far back as the 1500s, with some details presented by the Florida Fish and Wildlife timeline aligning with evidence presented in the publication.
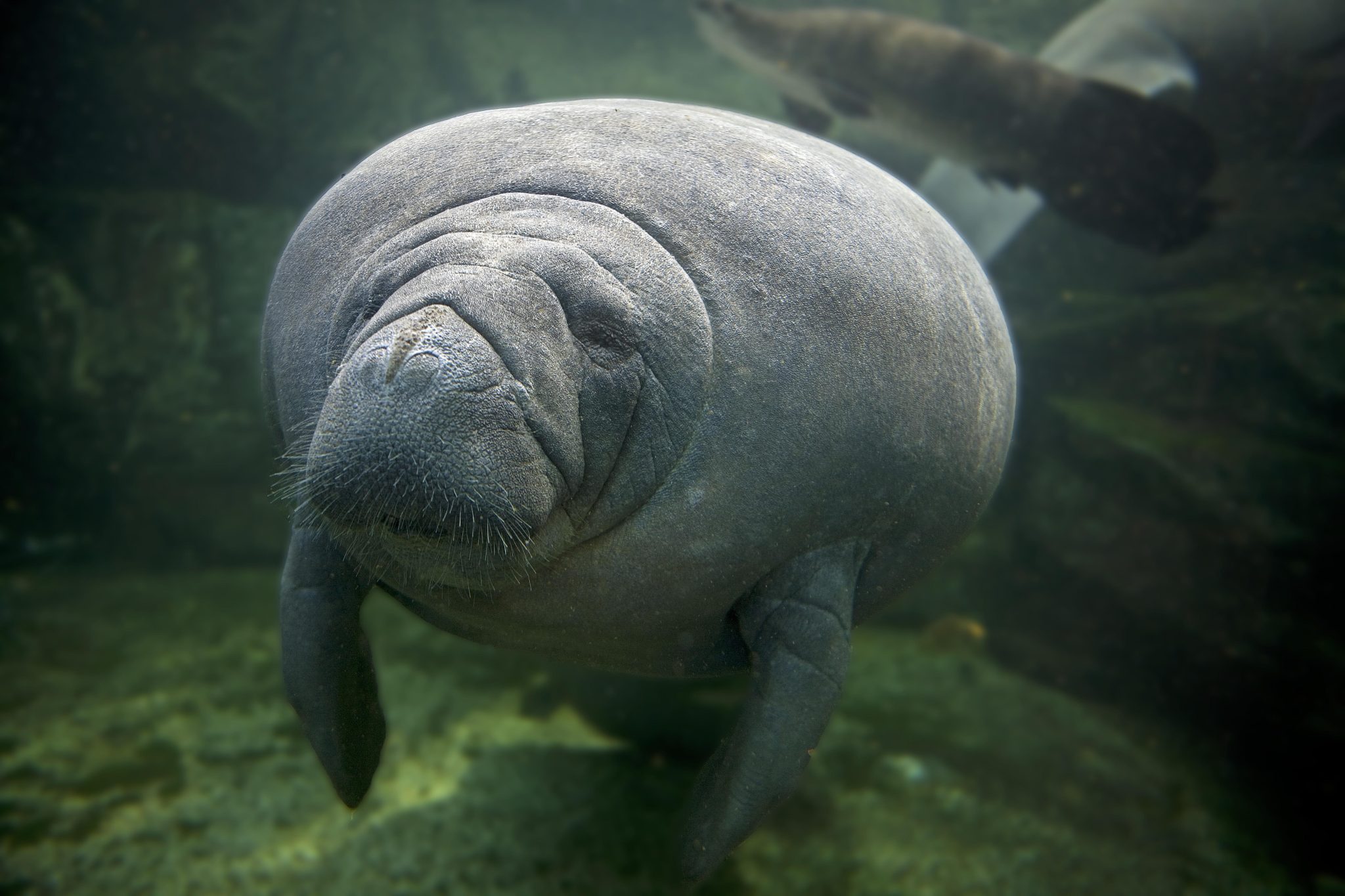

Manatee species, such as the African manatee and the Antillean manatee, continue to be poached by humans (Marsh et al., 2022). As a result, these species are difficult to observe in the wild and may adapt by foraging at night to avoid human encounters (Rycyk et al., 2021). This behavior could help explain why historical Florida manatee populations that were hunted by humans are absent from middens and rarely mentioned in historical accounts.
Further, the publication only briefly touches on the paleontological record and genetic evidence, which indicate that manatees have existed in Florida for a much longer period. Fossil and genetic evidence reveal a rich history of manatees in Florida. Manatees belong to the order Sirenia, which includes the Amazonian, African, and West Indian manatee species. While Sirenian fossils have been found globally, only Florida and the Caribbean contain specimens from every epoch over the past 50 million years (Reep and Bonde, 2006). The modern manatee, as we know it, emerged in the Caribbean about 2 million years ago (Domning, 1982).
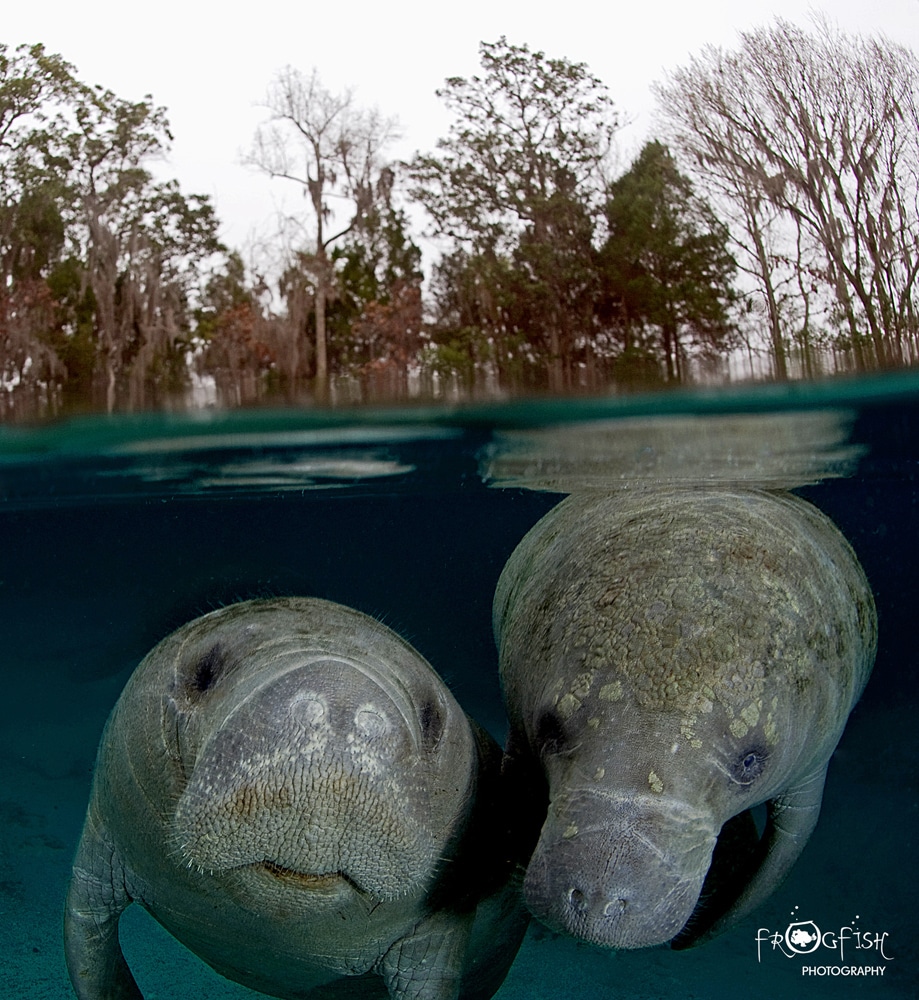

The evolution of manatees during the Pleistocene epoch provides valuable insights into how environmental changes shaped their distribution and genetic diversity. During the Pleistocene epoch (2.59 million to 11,700 years ago), there were roughly 20 cycles of long glacial periods (40,000–100,000 years) followed by shorter interglacial periods lasting around 20,000 years. At the start of these warmer periods, Caribbean manatees migrated northward with the warming waters (Reep and Bonde, 2006). Water currents and thermal barriers isolated these manatees from populations in Mexico and the Caribbean, leading to genetic divergence. Fossil evidence indicates that Trichechus manatus bakerorum lived in Florida and North Carolina about 125,000 years ago but did not survive the last glacial period, which began 100,000 to 85,000 years ago (Domning, 2005). This subspecies was eventually replaced by modern Florida manatees.
This evolutionary theory is further supported by genetic evidence. Research indicates that Florida manatees trace their evolutionary origins to Caribbean ancestors that migrated northward over the past 12,000 years (Garcia-Rodriguez et al., 1998). A 2012 study by Tucker et al. reinforces this theory, showing higher genetic diversity in manatees on Florida’s west coast compared to those on the east. Over time, core populations migrated northward, with some groups moving south and east along the Florida coastline before heading north along the Atlantic. This migration pattern left the west coast population with greater genetic diversity, while the east coast population retained only a smaller subset. These findings suggest that the founding population of Florida manatees—arriving approximately 12,000 years ago—originated along Florida’s southwestern coast, which became the center of the state’s manatee population (Reep and Bonde, 2006). The process of vicariance further supports this hypothesis; as geographic and ecological barriers emerged, they likely isolated the Florida manatee populations from their Caribbean ancestors. This isolation likely limited migration back and forth between regions, fostering the establishment of local populations in southwestern Florida.
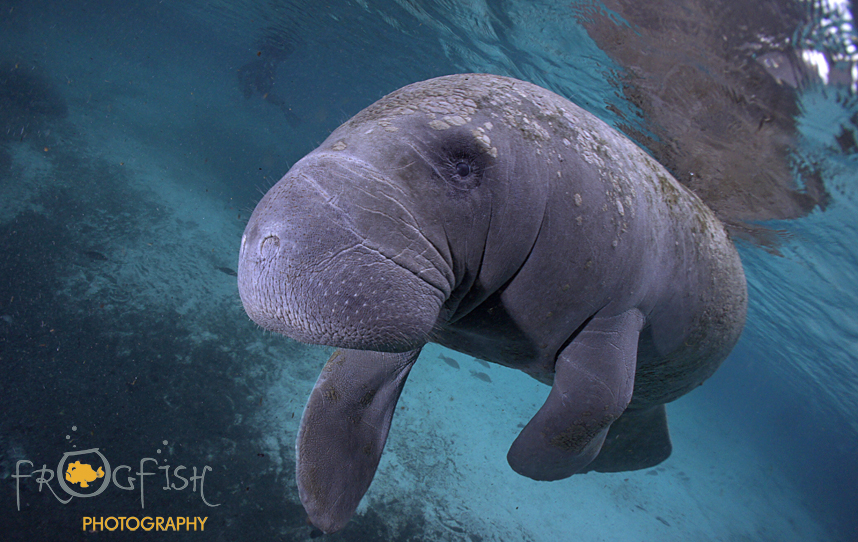

Manatees are not only a cherished symbol of Florida’s natural heritage but also a species with deep evolutionary and historical ties to the region. In sum, despite recent claims questioning their nativity, extensive fossil and genetic evidence confirms that manatees have been present in Florida’s waters for thousands of years, with ancestors dating back over 12,000 years. We agree with the authors of the published article that protecting these iconic creatures and their habitats is essential to preserving Florida’s unique ecological identity for future generations
Beth Brady is the Senior Science and Conservation Associate at Save the Manatee Club whose work focuses on manatee biology and conservation. She has her PhD from Florida Atlantic University and her Master’s in Marine Science from Nova Southeastern University.
Marine Life & Conservation
Paul Watson Released as Denmark Blocks Japan’s Extradition Bid

Renowned anti-whaling activist Paul Watson has been released from custody in Greenland after spending five months in detention. Denmark’s Justice Ministry rejected Japan’s request for his extradition, citing insufficient guarantees that his time already served in custody would be credited against any potential sentence.
The 74-year-old Canadian-American was arrested on July 21 in Nuuk, Greenland’s capital, when his ship docked to refuel. His arrest was based on a 2012 Japanese warrant related to a 2010 encounter in Antarctic waters. Japan alleged Watson obstructed operations and caused damage to a whaling research ship during efforts to disrupt illegal whaling. Watson has consistently denied these claims, maintaining his commitment to marine conservation.
Denmark, which oversees extradition matters for Greenland, concluded that while the legal conditions for extradition were met, the lack of assurances from Japan regarding time-served credit made extradition untenable.
In a video shared by his foundation, Watson expressed gratitude and relief, saying, “After five months, it’s good to be out… and good to know they’re not sending me to Japan.” He added that the most difficult part of his time in custody was being separated from his two young sons.
Watson is a pioneering figure in marine conservation, known for founding the Captain Paul Watson Foundation in 2022 after decades of activism with the Sea Shepherd Conservation Society. His bold efforts to defend marine life have earned him widespread support, including from celebrities and conservationists. His work has also been featured in the acclaimed reality TV series Whale Wars.
Watson’s lawyer, Jonas Christoffersen, praised the decision, stating, “We are happy and relieved that Paul Watson is now free.” He added that Watson is eager to reunite with his family and continue his vital work.
The arrest occurred while Watson’s vessel, the M/Y John Paul DeJoria, was en route to the North Pacific with a team of 26 volunteers to intercept a Japanese whaling ship. His foundation described the arrest as politically motivated and emphasized that Watson’s actions were focused on ending illegal whaling practices.
Japan resumed commercial whaling in 2019 after leaving the International Whaling Commission, asserting that whale meat is a cultural tradition. Conservationists, however, continue to challenge these practices, highlighting their impact on marine ecosystems.
Despite the challenges, Watson remains steadfast in his mission to protect marine life and bring attention to whaling practices. His dedication to ocean conservation has made him a globally respected advocate for the environment.
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoScubaverse Christmas Gift Guide 2024: Day 4
-

 Gear Reviews2 weeks ago
Gear Reviews2 weeks agoGear Review: SurfEars 4
-

 News2 months ago
News2 months agoSanta Divers take the Plunge for Charity
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoScubaverse Christmas Gift Guide 2024: Day 1
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoMeet Insta360 Ace Pro 2: Redefining Action Cameras With Unrivaled 8K Image Quality & Smarter AI
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoScubaverse Christmas Gift Guide 2024: Day 5
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoScubaverse Christmas Gift Guide 2024: Day 2
-

 Marine Life & Conservation1 month ago
Marine Life & Conservation1 month agoPaul Watson Released as Denmark Blocks Japan’s Extradition Bid